A simple integrated microfluidic platform for the research of hydrogels containing gradients in cell density induced breast cancer electrochemotherapy
发布时间:2023-03-01
点击次数:
- 发表刊物:
- Talanta
- 关键字:
- Microfluidic chip Hydrophobic Electrochemotherapy (ECT) Cell density
- 摘要:
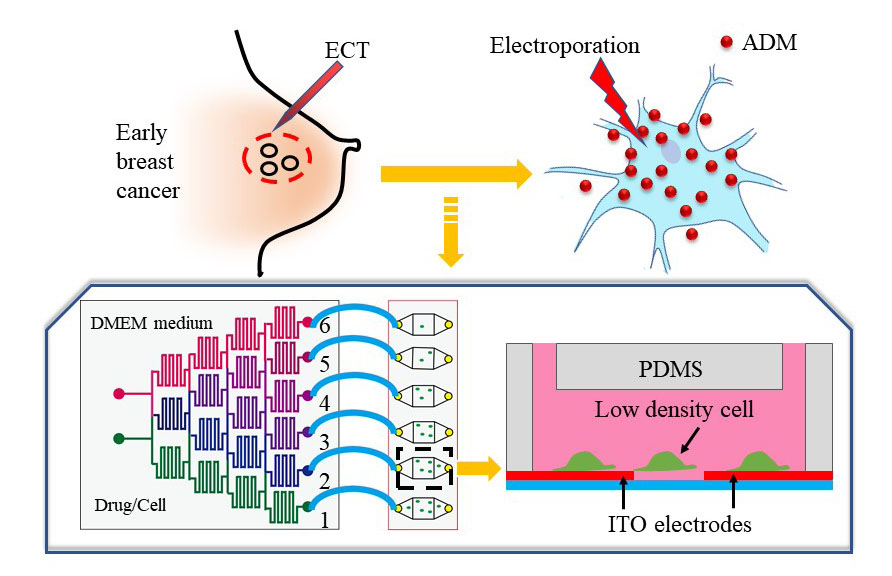
- Cell density is important for tumour metastasis, treatment and prognosis. Characterizing changes in cell density for electrochemotherapy (ECT) can reveal sub-populations in pathological states, and adjust treatment program. In this work, a simple and convenient microfluidic platform was developed to study the effect cell density on ECT by integrating the improved cell gradient generator, cell culture chamber and indium tin oxide interdigital electrodes. Agarose, as extracellular matrix (ECM), was used to 3D cell culture to imitate in vivo microenvironment. The precision and reproducibility of cell density gradient with agarose solution were achieved because the hydrophobic modification of microchannels surface resulted in reducing cell adhesion and residue. ECT cytotoxicity assay with difference in cell densities was studied. The results showed that tumour cell density is one of the most factors for ECT treatment and ECT cytotoxicity has a certain of cell density-depended. But only electroporation on low cell density level, ECM would be one of the most key factors for ECT cytotoxicity, which would provide a new idea for chip-based cell assay in clinical diagnosis and drug screening in ordinary laboratories.
- 论文类型:
- 期刊论文
- 是否译文:
- 否
- 发表时间:
- 2022-09-07
- 收录刊物:
- SCI
- DOI码:
- 10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123920
- 第一作者:
- Xuexia Lin
- 合写作者:
- Shufeng Zhou,Feixiang Fang,Chenjing Wang


